What are computer cookies? Are they secure ?
What is a cookie?
A cookie is a small file which is stored on users’ computer. Cookies hold a modest amount of data, specific to a particular client and website and can be accessed either by the web server or the client’s computer. This allows the server to deliver a page adapted to a particular user, or the page itself can contain some script which is aware of the data in the cookie and so can carry information from one visit to the website (or related site) to the next.

Types of cookies
It saves your session id and it exists only in temporary memory while the user navigates the website.
Web browsers normally delete session cookies when the user closes the browser.
A persistent cookie expires at a specific date or after a certain length of time.
The cookie’s lifespan can be as long or as short as its creators want.
The information will be transmitted to the server every time the user visits the website or every time the user views a resource belonging to that website from another website (such as an advertisement).
Persistent cookies are also referred to as tracking cookies because they can be used by advertisers to record information about a users’ web browsing habits over an extended period.
They are also used to keep users logged into their accounts on websites.
They reset if the expiration time is reached or the user manually deletes the cookie.
A secure cookie can only be transmitted over an encrypted connection.
This makes the cookie less likely to be exposed to cookie theft.
Supercookies can be a potential security concern and are therefore web browsers often block them.
If unblocked by the browser, an attacker in control of a malicious website could set a supercookie and potentially disrupt or impersonate legitimate user requests to another website that shares the same top-level domain or public suffix as the malicious website.
For example, a supercookie with an origin of .com could maliciously affect a request made to example.com, even if the cookie did not originate from example.com. This can be used to fake logins or to change users’ information.
It’s a cookie that automatically recreates itself after being deleted.
This happens by storing the cookie’s content in multiple locations, such as Flash Local object, HTML5 Web storage, and others.
When the cookie’s absence is detected, the cookie is recreated using the data stored in these locations.
Which cookies does my website use?
There are multiple ways to find that out.
We prefer to use a browser extension that tracks the cookies of your website live. It’s called EditThisCookie, and the extension is available for Google Chrome here and the Opera browser here.
As soon as you install it you’ll see a little cookie on your top right corner. Click on the cookie icon and it will tell you what cookies the website uses.
In the example below, we were on google.com.

What do all these cookies do?
There is a gigantic number of cookies out there, and it’s impossible to identify every single one of them.
You can use a database with the definition of the cookies, to help you understand the purpose of each cookie.
For example, you can visit Cookiepedia, it’s a database for cookies and it has an explanation for what they do.
You can search for the desired cookie then copy the description into your website to inform users of why you’re using those cookies. Although it is a very complete database, it might not have every single cookie. But, with a simple google search, you’ll find the purpose of a certain cookie.
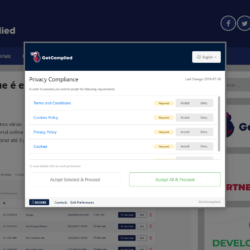
Find how to add cookies to your GDPR’s software GetComplied.
If you have any doubts don’t hesitate to talk to us!